Metric Base Unit For Length

The SI base of operations units are the standard units of measurement defined by the International Organisation of Units (SI) for the vii base quantities of what is now known every bit the International System of Quantities: they are notably a basic gear up from which all other SI units tin be derived. The units and their concrete quantities are the 2d for time, the metre for length or distance, the kilogram for mass, the ampere for electrical current, the kelvin for thermodynamic temperature, the mole for corporeality of substance, and the candela for luminous intensity. The SI base units are a central part of modern metrology, and thus part of the foundation of mod science and technology.
The SI base units class a set of mutually contained dimensions every bit required by dimensional assay commonly employed in science and applied science.[ citation needed ]
The names and symbols of SI base units are written in lowercase, except the symbols of those named afterwards a person, which are written with an initial capital letter. For instance, the metre has the symbol g, just the kelvin has symbol K, considering information technology is named after Lord Kelvin and the ampere with symbol A is named after André-Marie Ampère.
A number of other units, such as the litre, astronomical unit, and electronvolt, are not formally part of the SI, but are accustomed for use with SI.
Definitions [edit]
On xx May 2019, every bit the last act of the 2019 redefinition of the SI base units, the BIPM officially introduced the following new definitions, replacing the preceding definitions of the SI base units.
| Name | Symbol | Measure | Postal service-2019 formal definition[1] | Historical origin / justification | Dimension symbol |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| second | s | time | "The 2d, symbol south, is the SI unit of fourth dimension. It is defined by taking the fixed numerical value of the caesium frequency, ∆ν Cs, the unperturbed ground-state hyperfine transition frequency of the caesium 133 atom, to be ix192 631 770 when expressed in the unit Hz, which is equal to due south−1."[one] | The day is divided in 24 hours, each hour divided in threescore minutes, each minute divided in 60 seconds. A 2nd is 1 / (24 × 60 × threescore) of the day. Historically this day was defined as the hateful solar solar day; i.e., the average time between two successive occurrences of local credible solar apex. | T |
| metre | m | length | "The metre, symbol m, is the SI unit of length. It is defined past taking the fixed numerical value of the speed of light in vacuum c to be 299792 458 when expressed in the unit of measurement m s−1 , where the second is defined in terms of ∆ν Cs."[1] | ane / x000 000 of the distance from the Earth'south equator to the North Pole measured on the superlative arc through Paris. | L |
| kilogram | kg | mass | "The kilogram, symbol kg, is the SI unit of measurement of mass. It is defined by taking the fixed numerical value of the Planck constant h to exist 6.626070 15 ×10−34 when expressed in the unit J s, which is equal to kg mii south−one , where the metre and the 2nd are defined in terms of c and ∆ν Cs."[ane] | The mass of 1 litre of water at the temperature of melting ice. A litre is one thousandth of a cubic metre. | M |
| ampere | A | electric electric current | "The ampere, symbol A, is the SI unit of electric current. It is divers past taking the fixed numerical value of the simple accuse e to be 1.602176 634 ×10−xix when expressed in the unit C, which is equal to A south, where the second is defined in terms of ∆ν Cs."[1] | The original "International Ampere" was defined electrochemically equally the electric current required to eolith ane.118 milligrams of silver per second from a solution of silver nitrate. Compared to the SI ampere, the divergence is 0.015%. Nonetheless, the nearly contempo pre-2019 definition was: "The ampere is that constant current which, if maintained in two direct parallel conductors of infinite length, of negligible round cross-department, and placed one metre autonomously in vacuum, would produce between these conductors a forcefulness equal to 2×10−vii newtons per metre of length." This had the outcome of defining the vacuum permeability to be μ 0 = ivπ ×10−vii H/yard or Northward/A2 or T⋅m/A or Wb/(A⋅m) or 5⋅s/(A⋅thousand) | I |
| kelvin | K | thermodynamic temperature | "The kelvin, symbol M, is the SI unit of thermodynamic temperature. It is defined by taking the fixed numerical value of the Boltzmann constant thousand to exist 1.380649 ×10−23 when expressed in the unit of measurement J Thou−one , which is equal to kg mtwo southward−2 Thou−1 , where the kilogram, metre and second are defined in terms of h, c and ∆ν Cs."[1] | The Celsius scale: the Kelvin scale uses the caste Celsius for its unit increment, but is a thermodynamic scale (0 G is absolute zero). | Θ |
| mole | mol | amount of substance | "The mole, symbol mol, is the SI unit of measurement of corporeality of substance. One mole contains exactly vi.022 140 76 × x23 elementary entities. This number is the fixed numerical value of the Avogadro abiding, N A, when expressed in the unit mol−1 and is chosen the Avogadro number. The amount of substance, symbol n, of a system is a mensurate of the number of specified elementary entities. An elementary entity may be an atom, a molecule, an ion, an electron, any other particle or specified group of particles."[i] | Atomic weight or molecular weight divided by the molar mass constant, 1 yard/mol. | Due north |
| candela | cd | luminous intensity | "The candela, symbol cd, is the SI unit of measurement of luminous intensity in a given management. It is divers by taking the fixed numerical value of the luminous efficacy of monochromatic radiation of frequency 540×ten12 Hz, Chiliad cd, to exist 683 when expressed in the unit lm W−ane, which is equal to cd sr West−i , or cd sr kg−1 k−ii due south3 , where the kilogram, metre and second are defined in terms of h, c and ∆ν Cs."[1] | The candlepower, which is based on the lite emitted from a burning candle of standard backdrop. | J |
2019 redefinition of the SI base of operations units [edit]
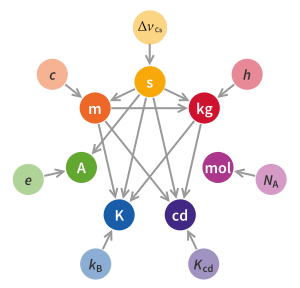
New SI: Dependence of base unit definitions on physical constants with fixed numerical values and on other base units that are derived from the same ready of constants. Arrows are shown in the reverse direction compared to typical dependency graphs, i.east. in this chart means depends on .

The SI system later on 1983, but before the 2019 redefinition: Dependence of base unit definitions on other base units (for case, the metre is defined every bit the altitude travelled by light in a specific fraction of a second), with the constants of nature and artefacts used to define them (such as the mass of the IPK for the kilogram).
New definitions of the base units were approved on 16 November 2018, and took effect 20 May 2019. The definitions of the base units have been modified several times since the Metre Convention in 1875, and new additions of base of operations units take occurred. Since the redefinition of the metre in 1960, the kilogram had been the only base unit still defined straight in terms of a physical artefact, rather than a holding of nature. This led to a number of the other SI base units being defined indirectly in terms of the mass of the same artefact; the mole, the ampere, and the candela were linked through their definitions to the mass of the International Image of the Kilogram, a roughly golfball-sized platinum–iridium cylinder stored in a vault almost Paris.
It has long been an objective in metrology to define the kilogram in terms of a primal abiding, in the aforementioned manner that the metre is now defined in terms of the speed of light. The 21st General Conference on Weights and Measures (CGPM, 1999) placed these efforts on an official footing, and recommended "that national laboratories continue their efforts to refine experiments that link the unit of mass to fundamental or diminutive constants with a view to a future redefinition of the kilogram". 2 possibilities attracted particular attention: the Planck constant and the Avogadro constant.
In 2005, the International Committee for Weights and Measures (CIPM) approved preparation of new definitions for the kilogram, the ampere, and the kelvin and it noted the possibility of a new definition of the mole based on the Avogadro constant.[2] The 23rd CGPM (2007) decided to postpone any formal modify until the next General Briefing in 2011.[3] [ needs update ]
In a note to the CIPM in October 2009,[iv] Ian Mills, the President of the CIPM Consultative Committee – Units (CCU) catalogued the uncertainties of the cardinal constants of physics according to the current definitions and their values under the proposed new definition. He urged the CIPM to accept the proposed changes in the definition of the kilogram, ampere, kelvin, and mole so that they are referenced to the values of the primal constants, namely the Planck constant (h), the electron charge (due east), the Boltzmann abiding (k), and the Avogadro constant (N A).[5] This approach was canonical in 2018, merely subsequently measurements of these constants were achieved with sufficient accuracy.
See also [edit]
- International vocabulary of metrology
- International System of Quantities
- Non-SI units mentioned in the SI
- Metric prefix
- Physical constant
References [edit]
- ^ a b c d e f g h "The International System of Units (SI), ninth Edition" (PDF). Bureau International des Poids et Mesures. 2019.
- ^ 94th Meeting of the International Committee for Weights and Measures (2005). Recommendation 1: Preparative steps towards new definitions of the kilogram, the ampere, the kelvin and the mole in terms of central constants Archived vii August 2011 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ 23rd General Conference on Weights and Measures (2007). Resolution 12: On the possible redefinition of certain base units of the International Organization of Units (SI).
- ^ Ian Mills, President of the CCU (October 2009). "Thoughts nigh the timing of the alter from the Current SI to the New SI" (PDF). CIPM. Retrieved 23 February 2010.
- ^ Ian Mills (29 September 2010). "Draft Chapter 2 for SI Brochure, following redefinitions of the base units" (PDF). CCU. Retrieved 1 January 2011.
External links [edit]
- International Agency of Weights and Measures
- National Physical Laboratory
- NIST -SI
Metric Base Unit For Length,
Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/SI_base_unit
Posted by: warrendanythas.blogspot.com





0 Response to "Metric Base Unit For Length"
Post a Comment